So it is again this time of year where you make a few pledges that you soon forget about. I am no exception to this rule, and formed three New Year Resolutions to date.
New Year Resolution #1: make more of my work public
This blog is of course a …
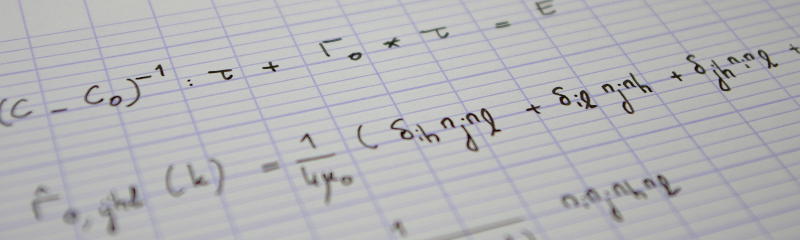
So it is again this time of year where you make a few pledges that you soon forget about. I am no exception to this rule, and formed three New Year Resolutions to date.
This blog is of course a …
Together with our post-doctoral fellow Othmane Zerhouni, my colleague Kostas Danas (LMS, École polytechnique) and I have recently published a new paper in International Journal of Engineering Science. The paper is titled “Quantifying the effect of two-point correlations on the effective elasticity of specific classes of random porous materials with …
In this post, we compute numeric values of the apparent stiffness introduced in this post. Our goal is to find the solution to the general problem depicted below.
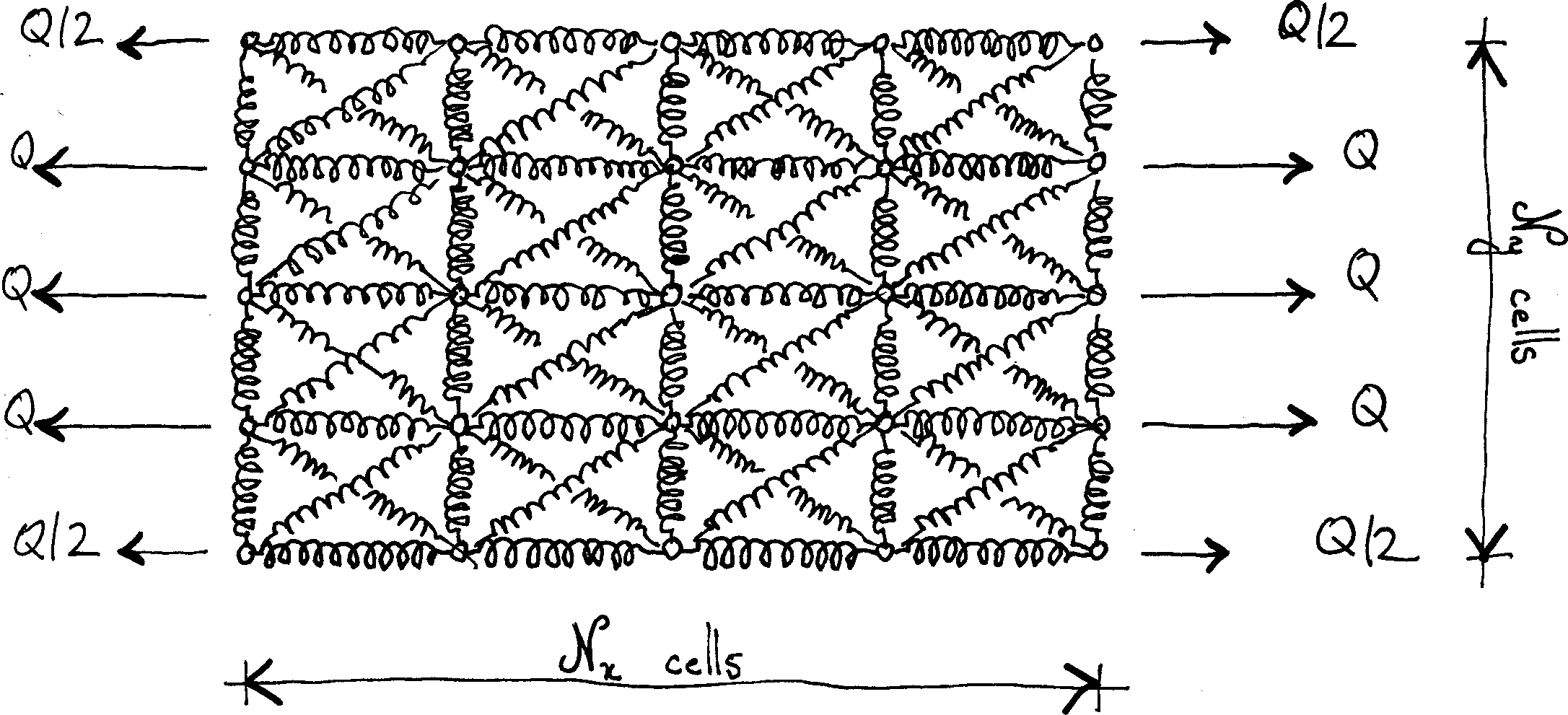
We use a numeric approach that is akin to the finite element method. More precisely, we minimize the total potential energy of …
In this post, we compute symbolic expressions of the apparent stiffness introduced in this post. Our goal is to find the solution to the general problem depicted below.

We consider a simplified case, where the mesh is square and vertical and horizontal springs have equal stiffnesses …
In the previous instalment of this series on homogenization, we derived the homogenized properties of a rectangular spring mesh. Our goal in this post is to analyse the “convergence” towards the homogenized stiffness; meanwhile, we will discuss the size of the so-called representative volume element (RVE).
In the previous instalment of this series on homogenization, we discussed volume and ensemble averages for random heterogeneous materials. In view of introducing statistical and representative volume elements, we will introduce in this post our first homogenization example, namely a two-dimensional, rectangular mesh of springs that is loaded in its …
This post is not going to be the most exciting I have ever written. We will derive the expression of the elastic energy of a linear spring as a function of the displacement of its two end-points. I will need this expression in my series on “What is homogenization”. Having …
In the previous instalment of this series on homogenization, we discussed homogenization of a distribution of black dots on a white background to a uniform shade of gray. In that example, homogenization boils down to evaluating the fraction of the total area occupied by the dots: this is the so-called …
In the previous instalment of this series, we introduced homogenization and the separation of scales. In the present post, we will discuss two strategies to carry out homogenization: the experimental and the theoretical approaches. To do so, we will again use the analogy with the halftoning technique.
Remember that we …
Most of my research activities deal with upscaling the mechanical properties of heterogeneous materials. This is also known as homogenization. So what is homogenization? This series explores this question; it is largely based on the introduction to my Habilitation defense.
In order to introduce homogenization, we will draw inspiration from …
In the previous instalment of this series, we implemented Moisan's (2011) efficient algorithm to compute the periodic-plus-smooth decomposition of an image. This algorithm relies heavily on the discrete Fourier transform, and already improves quite a lot over our previous conjugate gradient-based implementation. In the present post, we will show that …
In the previous instalment of this series, we computed Moisan's (2011) periodic-plus-smooth decomposition of an image by means of the conjugate gradient method. This worked like a charm, but was fairly inefficient, owing to the iterative nature of the method. Moisan actually showed that the whole decomposition could be computed …
In this post, we will compute Moisan's (2011) periodic-plus-smooth decomposition of an image by direct minimization of the energy introduced in the second instalment of this series. More precisely, $u$ being a $m\times n$ image, we will minimize the function $F(v, u)$ over the space of $m\times …
In the previous instalment of this series, we introduced the linear operators $Q_1$ and $Q$ that allow to define Moisan's (2011) periodic-plus-smooth decomposition $(p, s)$ of an image $u$ as follows
$$s=\operatorname*{arg\,min}_v F(v, u)\quad\text{and}\quad p=u-s,$$
with
$$F(v, u …
In the previous instalment of this series, we introduced the periodic-plus-smooth decomposition of an image as a pair of images which minimizes an energy functional. Observing that this energy is a quadratic form, the purpose of this post is to derive closed form expressions of the underlying linear operators. These …
In the previous instalment of this series, we discussed the need for periodic images. Although not all images are periodic, some image analysis techniques are best performed in Fourier space (using the fast Fourier transform). Applying Fourier-based techniques to images that are not periodic (as is often the case) generates …
In this new series, we will explore the so-called periodic-plus-smooth decomposition of an image, introduced by Moisan in 2011. This series is largely based on Moisan's paper, called Periodic plus Smooth Image Decomposition (the author's version can be found on HAL). Besides introducing a quite smart technique (that I do …
On monday 20th, november 2017 (at 13:30), I will be defending my "Habilitation à Diriger des Recherches" at École des Ponts ParisTech in front of the following jury
I recently had the pleasure to give a talk on “Variational estimates of the poroelastic coefficients” at the 6th Biot Conference on Poromechanics that took place at École des Ponts ParisTech on July 9-13, 2017. This is joint work with my colleague Siavash GHABEZLOO. It has been ongoing for years …
I am currently preparing with two other colleagues a review paper on X-ray tomography of cementitious materials, for which I need to retrieve tabulated values of the X-ray mass attenuation coefficients of all elements. NIST provides such data (see X-Ray Mass Attenuation Coefficients by J. H. Hubbell and S. M …
My student Mohamed Hassan Khalili has recently had one of his papers published in Physical Review E. The paper is called “A numerical study of one-dimensional compression of granular materials”. I have only been very marginally involved in this DEM study, which is divided in two parts.
Part I is …
Our paper “Discrete Digital Projections Correlation: a reconstruction-free method to quantify local kinematics in granular media by X-ray tomography” has recently been published in Experimental Mechanics. The abstract is reproduced below
We propose a new method to measure the translations and rotations of each individual grain in a granular material …
My paper “Towards improved Hashin--Shtrikman bounds on the effective moduli of random composites” has recently been published in Mechanics & Industry. The abstract is reproduced below
The celebrated bounds of Hashin and Shtrikman on the effective properties of composites are valid for a very wide class of materials. However, they incorporate …
In the previous instalment of this series, we have analyzed the morphology of the rice grains. In particular, we have defined their orientation as that of the major axis of inertia. We are now in a position to quantify the statistics of the orientations. We will first discuss one-point statistics …
My paper “Reconstructing displacements from the solution to the periodic Lippmann--Schwinger equation discretized on a uniform grid” has recently been published in International Journal of Numerical Methods in Engineering. The abstract is reproduced below
Uniform grid solvers of the periodic Lippmann--Schwinger equation have been introduced by Moulinec and Suquet for …
$\newcommand{\tens}{\mathbf}\newcommand{\D}{\mathrm{d}}$
In the previous instalment of this series, we have segmented the 3D image of the assembly of rice grains. In other words, each voxel of the image is attributed the label of the grain to which it belongs. Remember the initial goal of …
My student Vinh Phuc Tran has recently had one of his papers published in Mechanics of Materials. The paper is called Stochastic modeling of mesoscopic elasticity random field. The abstract is reproduced below
In the homogenization setting, the effective properties of a heterogeneous material can be retrieved from the solution …
In the previous instalment of this series, I showed that a convincing binary image could be produced from the gray level 3D reconstruction of the assembly of rice grains, using Otsu's threshold. However, I intend to carry out statistical analyses of the grains themselves in the subsequent instalments. Therefore, instead …
In the previous instalment of this series, we used the circle Hough transform to find the boundary of the sample and define the circular ROI. Within this ROI, we now need to segment the rice grains. In other words, starting from a gray-level image (Fig. 1, left), we want to …
Finding the stress resultant and stress couple in a spherical pressure vessel seems easy enough. Well, this apparently simple problem allows us to highlight subtle thickness effects within shells. It should be emphasized again that these thickness effects have nothing to do with shear corrections. Indeed, shear stresses are null …
In the previous instalment of this series, we analysed a spherical pressure vessel by means of Koiter's linear theory of thin shells. We found the somewhat unexpected result that the stress couple was not null. Besides, we also found that the stress resultant was slightly different from the well-known value …
In structural analysis, thick beams (resp. plates) usually refer to shear deformability, and the Timoshenko beam theory (resp. Mindlin–Reissner plate theory). With curved elements however (e.g. curved beams or shells), the situation is more subtle, as thickness corrections may be necessary even in shells where the shear stress …
In the previous instalment of this series, we obtained binned slices of the sample. Fig. 1 below displays a typical example of these binned slices. We now want to segment the rice grains. However, the analysis (in particular, Otsu thresholding) might be perturbed by the fact that the walls of …
The full reconstructed image resulting from the tomography experiment described in the second instalment of this series is a 1747×1751×688 stack. The voxel size is about 0.030 mm. This is far too much for the purpose of the present study, since all we are interested in is the determination …
In the first instalment of this series, I briefly introduced orientational order in assemblies of anisotropic particles, and proposed an illustration based on synthetic microstructures. But what I really intend to do in this series is to show how orientational order can be quantified in a “real-life” sample, namely a …
In this series, I will explore the notion of orientational order in random packings of anisotropic (flat or elongated), hard particles. By orientational order, I mean that particles which are close to each other tend to adopt the same orientation. This leads to strong local anisotropy, while the packing may …
In a previous post, I introduced the fourth-rank spherical and deviatoric projection tensors. Any isotropic fourth-rank tensor is a linear combination of these two tensors; in other words, the space of isotropic fourth-rank tensors (with minor and major symmetries) is of dimension 2. Similarly, it can be shown (Walpole, 1984 …
The double dot product of two tensors is the contraction of these tensors with respect to the last two indices of the first one, and the first two indices of the second one. Whether or not this contraction is performed on the closest indices is a matter of convention. In …
In this post, I will introduce the acoustic tensor of linearly elastic materials. Closed-form expressions of the inverse of this tensor can be derived in the case of isotropic materials. This will later come in handy to derive closed-form expressions of the periodic Green operator for strains.
We consider a …
In the previous instalments of this series (see Part 1 and Part 2), I have shown that regardless of the dimensionality (3D or plane strain elasticity), the constitutive law of an isotropically elastic material reads
$$\sigma_{ij}=\kappa\varepsilon_{kk}\delta_{ij}+2\mu\left(\varepsilon_{ij}-\frac{\varepsilon_{kk …
I recently scanned a document as a PDF file, and I wanted to retrieve
the embedded images. I really mean extract the images, and not
convert the pages of the document to images (which would entail loss
of data). There is a nice command-line tool to do that: pdfimages,
which …
In the previous instalment of this series, I introduced the constitutive law of an isotropically elastic material, and the related material constants, within the framework of 3D elasticity. I will now address the case of plane strain elasticity.
Problems of plane strain elasticity are defined as problems where the following …
Among all classes of materials, the class of linearly elastic and isotropic materials is probably the simplest. Such materials are defined by two elastic constants: for example, Young\'s modulus $E$ and Poisson\'s ratio $\nu$. However, depending on the situation, this pair of constants might not be the most …
One of my manuscripts has just been accepted for publication in the International Journal of Solids and Structures. It is called A variational form of the equivalent inclusion method for numerical homogenization. The abstract is reproduced below
Due to its relatively low computational cost, the equivalent inclusion method is an …
It is my pleasure to announce that one of my papers has recently been accepted for publication in the Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. It's called New boundary conditions for the computation of the apparent stiffness of statistical volume elements.
It introduces a new set of boundary …